Git For beginners and 10 git commands
Beginners guide to git and 10 basic commands to get started.
Introduction
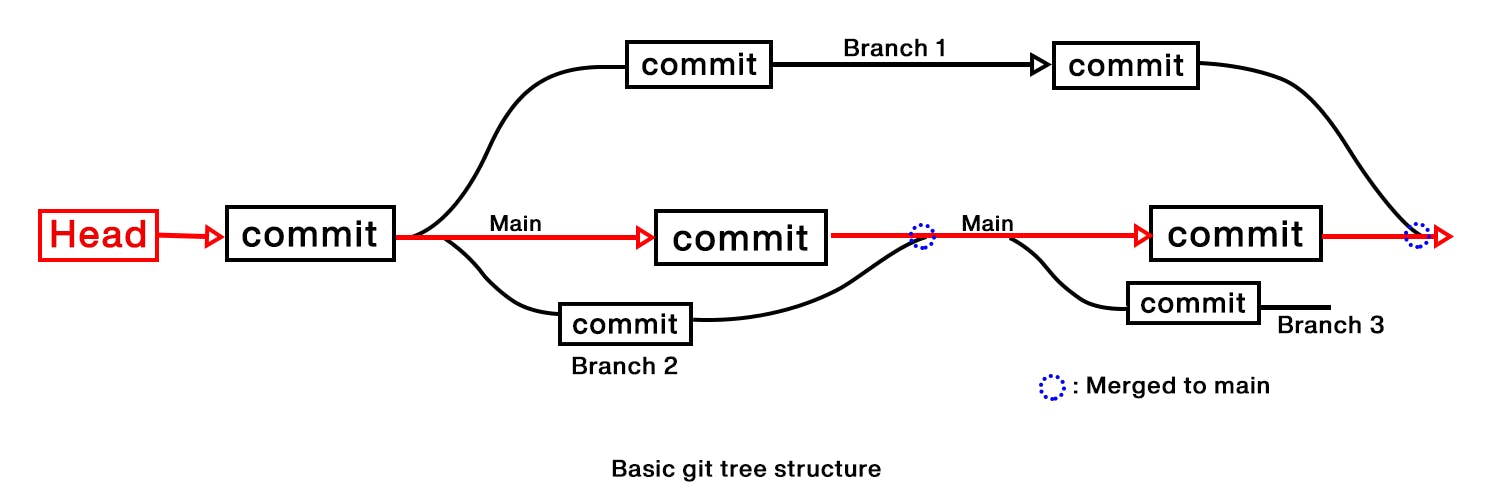
Git is an opensource version control system. It is a tool that is used to monitor changes in a git repository and allows various functionalities. A Git repository is a tree-like structure where it has a head that point to the main/master branch of the repository, and other branches are created from the main/master branch, changes are made and committed, and then merged to the main/master branch.
Few keywords to note
Branches
In a version control system, there is a head that point to the main branch after that we can at any point create a new branch from the main branch to make new features and test them thoroughly. We can create as many branches as we want.
Local
Anything that is stored on your working machine offline. Eg a local repository is a repository stored on your computer.
Remote
Anything that is stored on cloud or remote location and needs internet access to interact with it. Eg a remote repository would be a repository stored on Github.
Staging area
when changes are made in the git tracked repository, they are added to the area to preview them before saving(track) them. This area is the Staging area.
Commit
When changes are staged and ready to be saved(tracked) we commit those which create the snapshot of the commit along a timeline to maintain the history of git repository.
Commands:
Git init
This command is the first used to convert an unsupervised folder/ repository into git controlled repository.
Detailed info : link.
Git add:
This command is used to add the changes made in the git repository to the staging area. To add all the changes across multiple files you can use git add . or to add changes made in a particular file you can use git add .
Detailed info: link.
Git commit:
this command is used to commit changes in the staging area. It can be understood as each commit as a checkpoint in games and if anything goes wrong you can revert back to the last commit or previous commits.
Detailed info: link.
Git push:
this command is used to upload all the changes made on the local repository to the remote repository on GitHub, bitbucket, code commit, etc.
Detailed info: link
Git status:
this command shows the status of the files if any changes are made if the changes have been added to the staging area or not. Shows the current working status of the tree.
Detailed info: link
Git log:
This command shows all the commit history. This command is used to check the commit history and get the commit’s hash to revert, rebase, or any other purpose. The output is given in reverse chronological order by default.
Detailed info: link
Git branch:
There are various ways to use this command. It can be used to list the branches, make a new branch, and delete a branch.
Detailed info: link
Git checkout:
This command is used to switch between branches. To go from the current working branch to other branches in the repository
Detailed info: link
Git clone:
this command is used to clone the repository from remote location to local system.
Detailed info: link
Git pull:
This command is used to download or fetch the changes from remote repository to a current local branch. This is used when the remote branch is ahead of current branch.
Detailed info: link
These are just a few basic and most frequently used commands that you need to know to get started with git and explore more as you start using it.